How Wireless Works
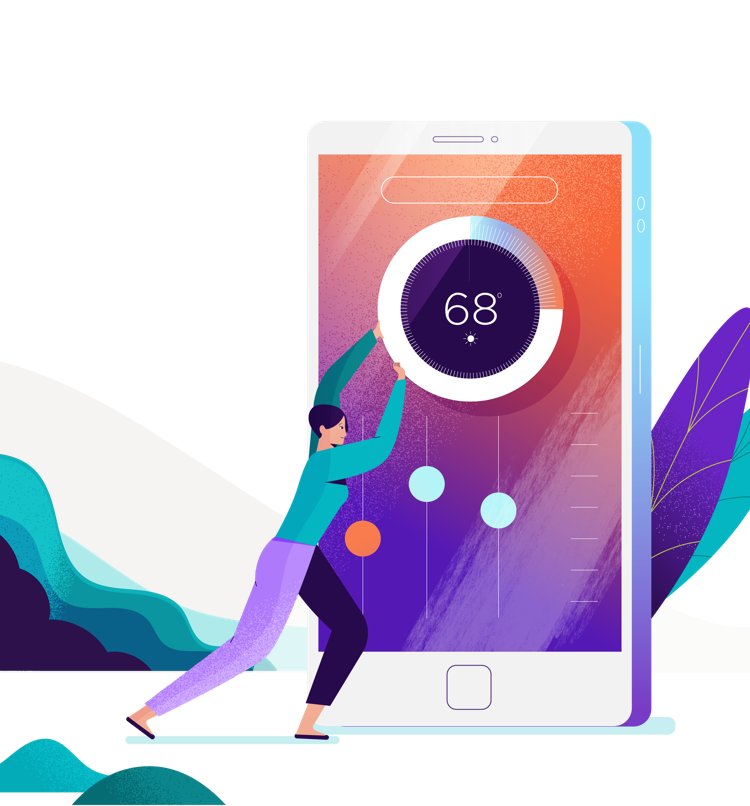

In the blink of an eye, your wireless device can send a text, order takeout, or adjust the temperature in your house from thousands of miles away. But have you ever wondered... how?
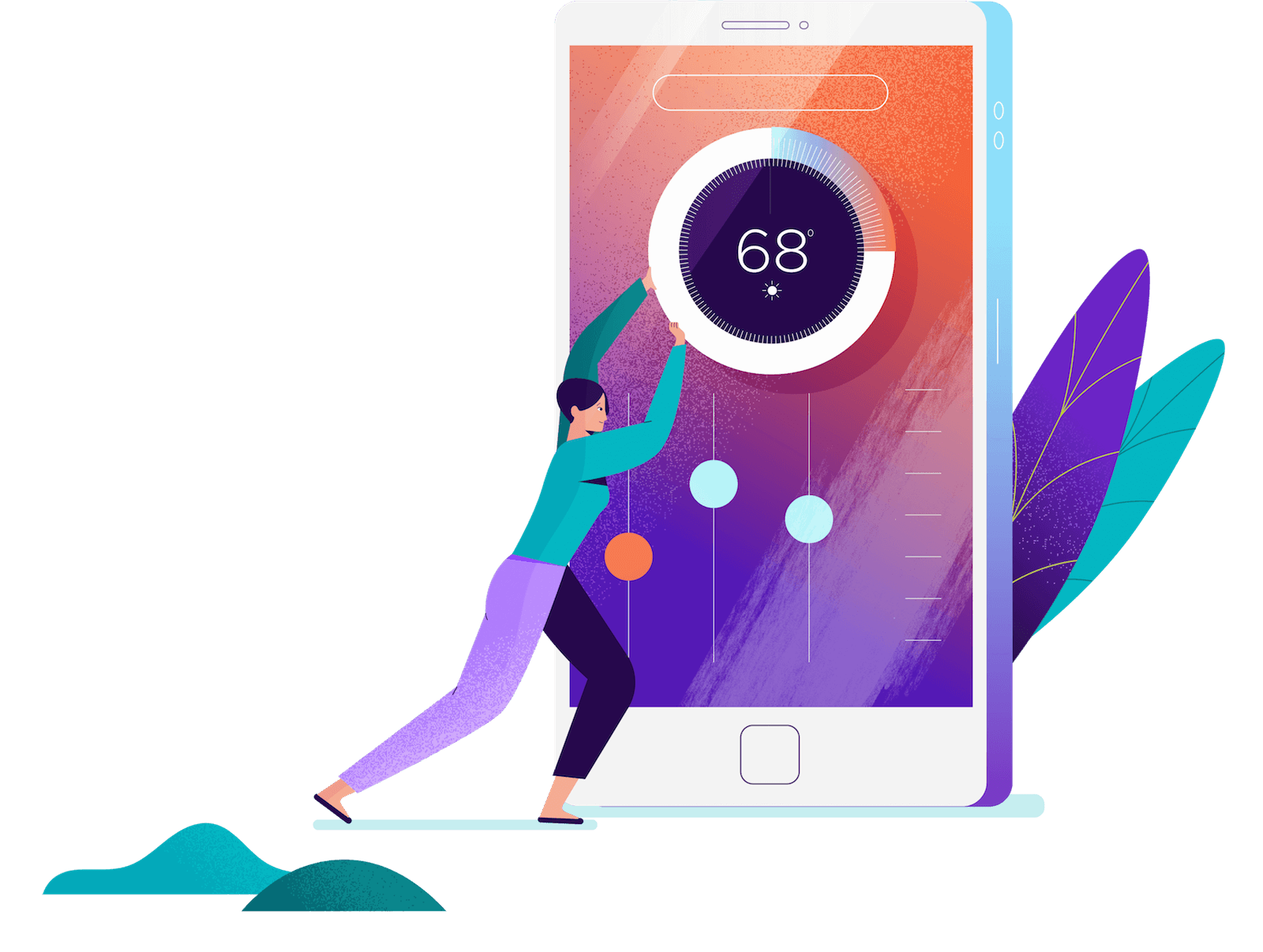





Follow the wireless journey from phone to thermostat.
When you take an action like adjusting the temperature on your smart thermostat from a remote location using a mobile device, you set off a series of events. And they all take place within a fraction of a few seconds.

Using a mobile app, your phone sends a signal.
Did You Know?1/2
Digitizing your voice
When you talk into your phone, your voice is digitized, converted into data packets, and sent over the air and through the network.
Did You Know?2/2
Just like a body, wireless networks are made of cells.
If you’re located within range of a particular cell site, congrats, you’re in the network. As you move about your life, nearing one cell site to the next, this network keeps you connected.

That signal gets sent over waves called spectrum.

Then it arrives at a nearby cell site.
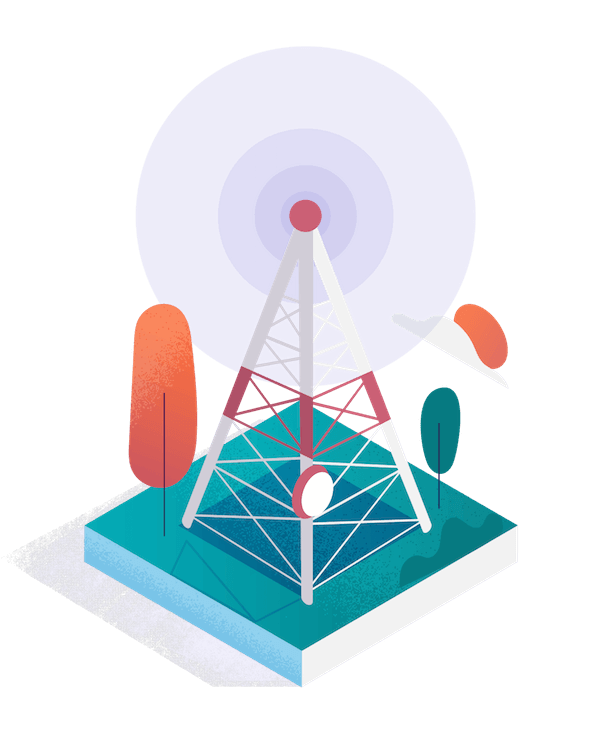
Cell Towers
Wide Coverage, High Capacity.
These towers can be up to 200+ feet tall, providing coverage over large geographic areas.
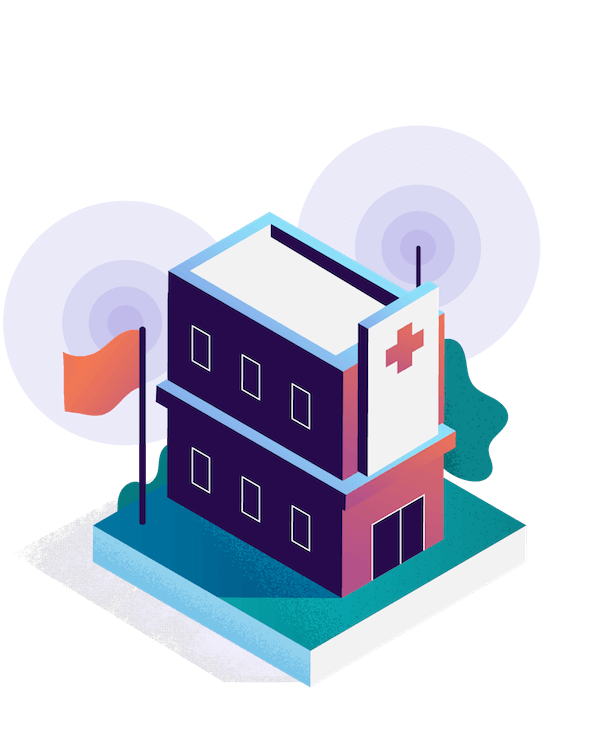
Roof Top Sites
Higher Capacity, Medium Coverage.
Often mounted in elevated spots like rooftops, these provide good coverage and enhance network capacity.
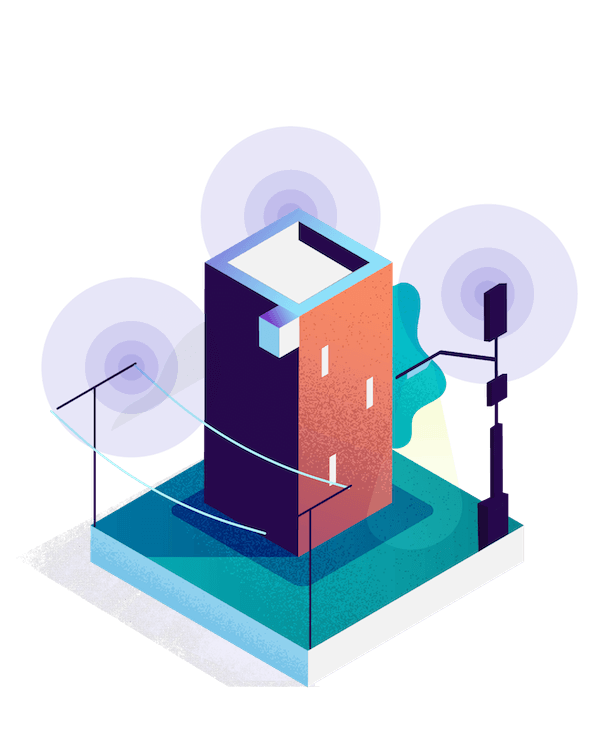
Small Cells
Higher Capacity, Lower Coverage.
Just the size of a backpack, small cells are often mounted on streetlights and lamp posts, providing higher capacity but covering smaller coverage areas like city blocks.
Did You Know?
Demand Is Rising.
There are over 447,000 active cell sites in operation today, built over 30+ years.
Did You Know?
Wireless networks operate on a grid made of cells.
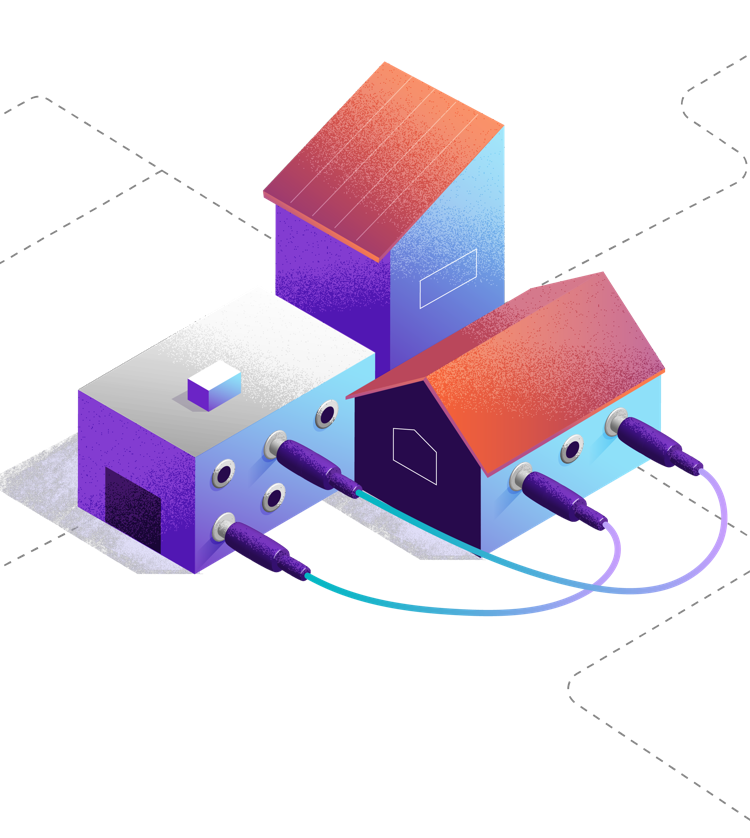

The signal travels to a network switch or router.


Your provider locates the cell site closest to your home.


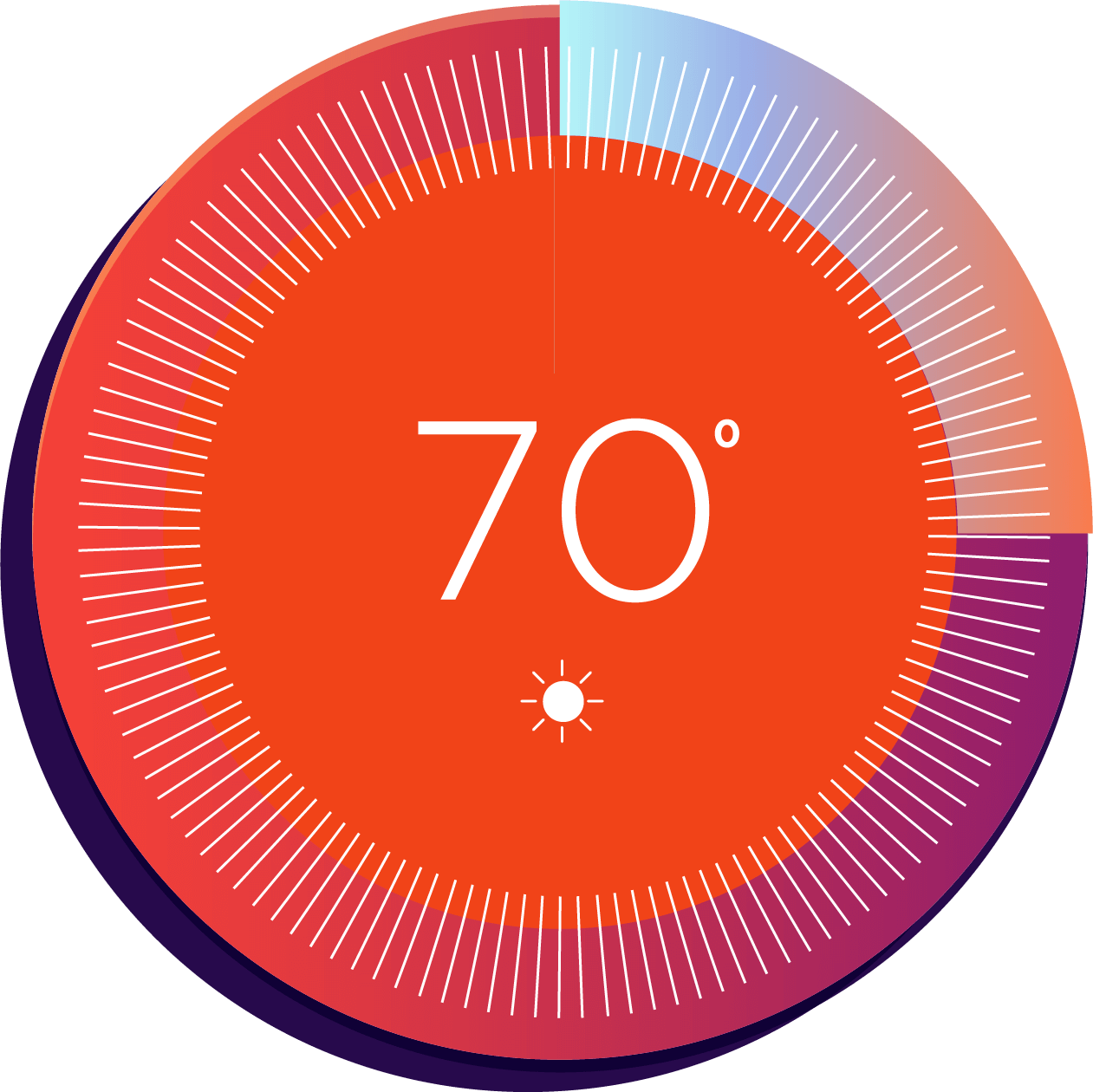
Signal received. Turn it up!
Did You Know?
IoT is still the next big thing.
Today, there are over 3.5 IoT devices for every human on earth, making it the fastest growing technology field ever.
The future is 5G.